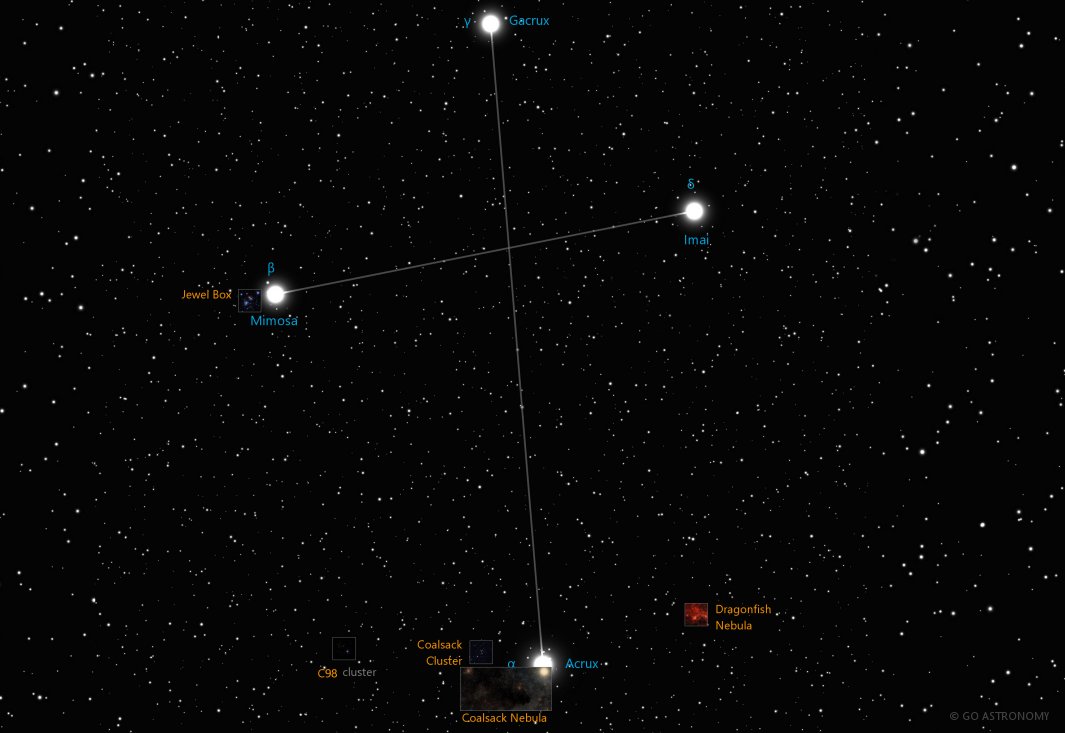
Crux, the Southern Cross (Cru)
(crucks)
The Southern constellation of Crux, the Southern Cross, is best viewed in Spring during the month of May.
Crux is the 88th largest constellation. It's brightest star is Acrux at magnitude 0.87. The boundary of the Crux constellation contains 3 stars that host known exoplanets.
Crux is a circumpolar constellation, so is visible year-round in the Southern hemisphere. Conversely, it is not visible in the opposite hemisphere.
- Pronunciation:
- crucks
- Meaning:
- Southern Cross
- Genitive:
- Crucis
- Abbreviation:
- Cru
- Constellation Family:
- Hercules
- Hemisphere:
- Southern
- Quadrant:
- SQ3
- Visibility:
- 20° N - 90° S
- Best viewing month*:
- May
- Area:
- 68 sq. degrees
- Size:
- 88th largest
- Circumpolar** (N=northern, S=southern):
- S circumpolar
- Right Ascension (avg):
- 12h 29m
- Declination (avg):
- -60°
- Brightest star:
- Acrux (0.87)
- Stars with planets:
- 3
- X-ray stars:
- 4 (2 binaries) stars
- Messier objects:
- |
Brightest Stars in Crux
The 10 brightest stars in the constellation Crux by magnitude.
- Star
- Magnitude
- Spectral class
- Beta Crucis (β Cru)
- 1.25
- B0.5III
- Alpha Crucis A (α1 Cru A)
- 1.4
- B0.5IV
- Gamma Crucis (γ Cru)
- 1.6
- M4III
- Alpha Crucis B (α2 Cru B)
- 2.09
- B1V
- Delta Crucis (δ Cru)
- 2.79
- B2IV
- Epsilon Crucis (ε Cru)
- 3.59
- K3/K4III
- Mu Crucis (μ1 Cru)
- 4.03
- B2IV-V
- Zeta Crucis (ζ Cru)
- 4.06
- B2.5V
- Eta Crucis (η Cru)
- 4.14
- F2III
- Theta Crucis (θ1 Cru)
- 4.32
- Am
Star Clusters in Crux
The most notable and easy-to-find star clusters in the constellation Crux . Also see all star clusters.
Nebulae in Crux
Notable and easy-to-find nebulae in the constellation Crux. Also see all nebulae.
Neutron Stars in Crux
These are the most well-known neutron stars in the constellation Crux. Although neutron stars cannot be seen in any amateur telescope, they are at the center of many supernova remnant nebulae, which can be seen. Also see all neutron stars.
The Southern Celestial Cross
Crux, more popularly known as the Southern Cross, is among the smallest yet most famous constellations in the night sky. With its distinctive cross-shaped star pattern, it is a prominent feature in the southern hemisphere and has great cultural and navigational significance.
Historical Background
The constellation Crux has been recognized and revered by many ancient cultures. European explorers, for instance, relied on it for celestial navigation during their voyages to the southern hemisphere. In contrast, for the indigenous people of Australia and New Zealand, the constellation holds a special place in their folklore and storytelling. Crux was not always visible from the Northern Hemisphere. Still, due to the precession of the equinoxes, it has now moved below the horizon for most northern observers.
Main Features and Location
Crux is nestled within the Milky Way's bright band and is located in the third quadrant of the southern hemisphere (SQ3). It can be observed at latitudes between +20? and -90?. The constellation is surrounded by Centaurus, which encircles it on three sides, and by Musca to the south.
Despite its small size, Crux is quite distinctive because it includes four bright stars - Acrux (Alpha Crucis), Mimosa (Beta Crucis), Gacrux (Gamma Crucis), and Imai (Delta Crucis) - that form an asterism known as the Southern Cross. An additional star, Ginan (Epsilon Crucis), is also often included in depictions of the constellation. Alpha Crucis, a multiple star system located approximately 321 light-years away from Earth, is the brightest star in the constellation and the 13th brightest star in the night sky.
Deep Sky Objects
The constellation Crux also houses a variety of interesting deep-sky objects. The Coalsack Nebula, a dark nebula that creates a striking silhouette against the Milky Way's bright star fields, is the most prominent. It is visible to the naked eye and appears as a large, dark patch in the southern part of the Milky Way.
Crux also contains the open cluster NGC 4755, also known as the Jewel Box or Kappa Crucis Cluster, which is one of the youngest known open clusters and has an estimated age of only 14 million years. With a magnitude of 4.2, it's visible to the naked eye under dark skies, but binoculars or a small telescope will reveal its true splendor.
Observation
For observers in the southern hemisphere, Crux is circumpolar, meaning it never sets below the horizon and is visible year-round. However, it is at its highest in the sky during the month of May. The constellation is often used for navigation, as drawing a line through the long axis of the cross points towards the South Celestial Pole.
In the Northern Hemisphere, Crux can only be seen in lower latitudes, near the southern horizon in the spring. For those in the mid-northern latitudes, Crux is below the horizon and not visible.
* Constellation shown for northen hemisphere skies. For the southern hemisphere, constellations appear rotated 180 degrees (upside-down and left-right reversed) from what is shown. Remember that seasons are reversed too - summer in northern latitudes is winter in southern latitudes.
** Circumpolar constellations are visible year-round in the hemisphere listed (and not at all in the opposite hemisphere).